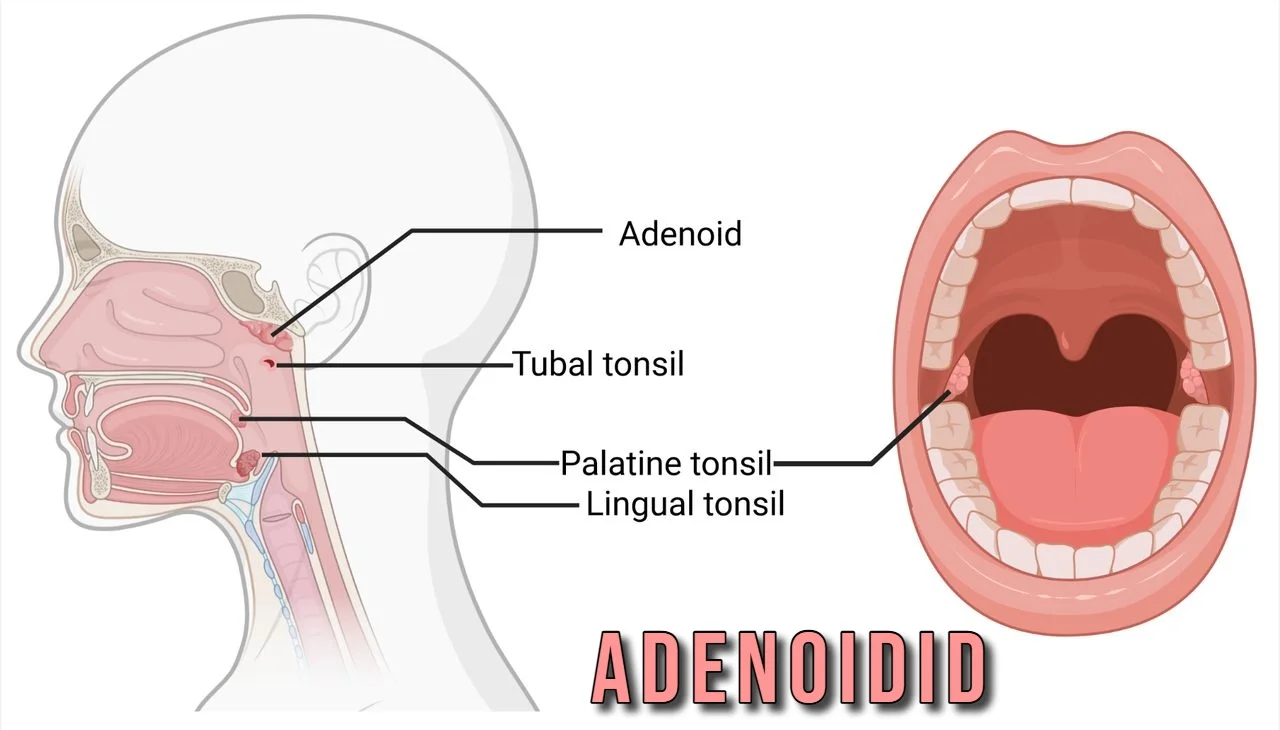
The human body has several defense mechanisms that protect us from infections. One of these is the adenoids, a small mass of lymphatic tissue located behind the nose and above the throat. When these tissues become inflamed or infected, the condition is known as Adenoidid.
Adenoidid is common in children but can also affect adults. It often leads to breathing difficulties, snoring, and recurrent infections, making early diagnosis and treatment essential.
What Is Adenoidid?
Adenoidid refers to inflammation of the adenoids, usually caused by a bacterial or viral infection.
The adenoids play a role in the immune system by trapping pathogens that enter through the nose or mouth. However, when they become enlarged or infected, they can create more problems than they solve.
Causes of Adenoidid
The main causes of Adenoidid include:
-
Infections – Viruses such as the common cold or bacteria like Streptococcus often trigger inflammation.
-
Allergies – Allergic reactions may cause chronic swelling of the adenoids.
-
Poor Immune Function – Children with weaker immune systems may be more prone.
-
Recurrent Upper Respiratory Infections – Frequent colds can contribute to chronic adenoid problems.
Symptoms of Adenoidid
Adenoidid can present with various symptoms, including:
-
Nasal congestion or blocked nose
-
Breathing through the mouth
-
Loud snoring or sleep apnea
-
Chronic ear infections
-
Sore throat or difficulty swallowing
-
Swollen glands in the neck
-
Restless sleep and daytime fatigue
In children, persistent Adenoidid may also affect speech development and facial growth, making it an important condition to address early.
Diagnosis of Adenoidid
Doctors may use several methods to diagnose Adenoidid:
-
Medical history and symptom check
-
Physical examination of the throat and nose
-
Endoscopy – using a small camera to visualize the adenoids
-
X-rays – to determine the size of enlarged adenoids
-
Lab tests – in cases of recurrent infections
Treatment Options for Adenoidid
1. Medications
-
Antibiotics – for bacterial infections.
-
Nasal sprays – to reduce swelling and congestion.
-
Pain relievers – to manage discomfort.
2. Home Care
-
Warm fluids and rest.
-
Humidifiers to keep airways moist.
-
Saline nasal rinses.
3. Surgery (Adenoidectomy)
When Adenoidid becomes chronic or severely impacts breathing and sleep, doctors may recommend surgical removal of the adenoids. This is a common and safe procedure in children, often combined with tonsil removal if both are enlarged.
Complications of Untreated Adenoidid
If left untreated, Ad-enoidid may cause:
-
Chronic ear infections and potential hearing loss.
-
Obstructive sleep apnea due to blocked airways.
-
Speech and developmental delays in children.
-
Sinus infections and recurrent throat infections.
Prevention of Adenoidid
While not all cases can be prevented, some steps may reduce risk:
-
Maintaining good hygiene (handwashing, sanitization).
-
Strengthening the immune system with proper nutrition and rest.
-
Treating allergies and infections early.
-
Avoiding exposure to smoke and pollutants, which irritate airways.
Adenoidid in Children vs. Adults
In Children
-
Most common between ages 3 and 7.
-
Can impact growth, sleep, and learning if untreated.
-
Surgery is often more effective at this age.
In Adults
-
Rare, but when present, it may indicate chronic infections or underlying health issues.
-
Requires thorough examination to rule out serious causes.
Living with Adenoidid
Families managing Ad-enoidid should:
-
Monitor symptoms closely.
-
Ensure children sleep comfortably (sometimes using an elevated pillow).
-
Follow up with healthcare providers for regular check-ups.
-
Consider lifestyle changes, such as allergy management and healthy routines.
Future Outlook
With medical advances, treatment for Ad-enoidid is safer and more effective than ever. Research continues to explore minimally invasive procedures and long-term preventive strategies to improve quality of life for children and adults alike.
Conclusion
Adenoidid is a common but manageable condition that affects the adenoids, leading to breathing problems, infections, and sleep disturbances. With early diagnosis, proper treatment, and—when necessary—surgery, most patients recover fully and enjoy a healthier life.
Parents, in particular, should watch for symptoms in children and consult healthcare providers promptly. Addressing Ad-enoidid early can prevent complications and support proper growth, sleep, and development.